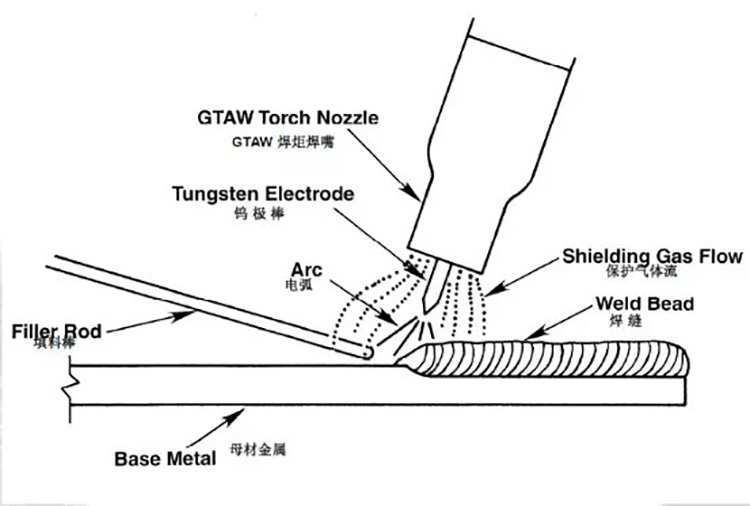
Argon tungsten arc welding uses argon as a shielding gas to heat and melt the welding material itself (it is also melted when the filler metal is added) by means of the arc generated between the tungsten electrode and the weld body, and then forms the welding of the weld metal Way. The tungsten electrode, weld pool, arc and joint seam area heated by the arc are protected from atmospheric contamination by the argon flow.
During argon arc welding, the relative positions of the torch, filler metal and weldment are as shown in the figure below: the arc length is generally 1~1.5 times the diameter of the tungsten electrode. When the welding is stopped, the filler metal is first extracted from the molten pool (the filler metal is added according to the thickness of the weldment), and the hot end still needs to stay under the protection of the argon flow to prevent its oxidation.
1. Welding torch (torch)
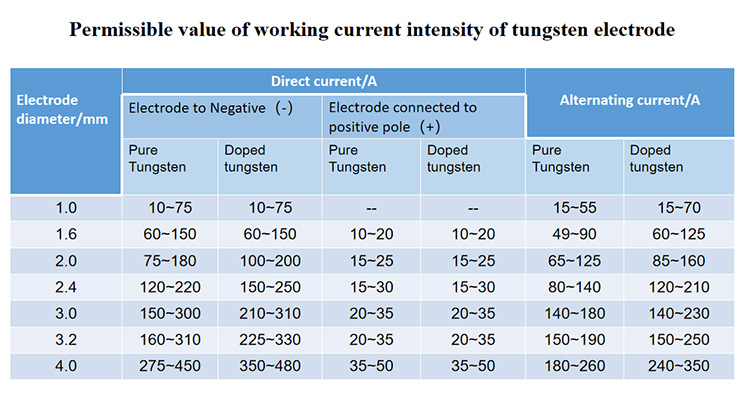
In addition to clamping the tungsten electrode and delivering the welding current, the argon tungsten arc welding torch (also known as the welding torch) also needs to spray shielding gas. High-current welding guns need to use water-cooled welding guns for long-term welding. Therefore, the correct use and protection of the welding torch is very important. Tungsten electrode load current capacity (A) is shown in the table below.
2. Gas path
The gas route is composed of argon cylinder pressure reducing valve, flow meter, hose and electromagnetic gas valve (inside the welding machine). The pressure reducing valve is used to reduce pressure and adjust the pressure of the protective gas. The flowmeter is used to calibrate and adjust the shielding gas flow. Argon arc welding machines usually use a combined decompression flowmeter, which is convenient and reliable to use.
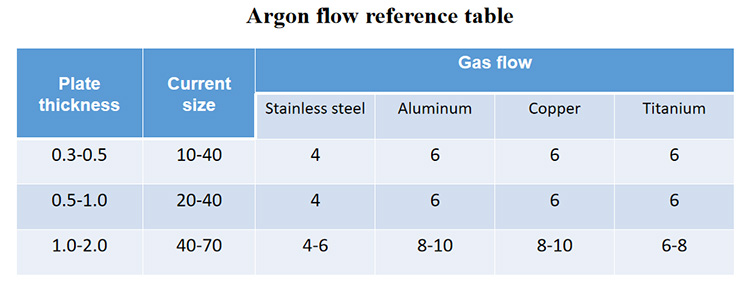
During argon arc welding, the requirement for the purity of argon gas is that the chromium-nickel stainless steel should be ≥99.7%, and the refractory metal should be ≥99.98%.
(1) Argon is an inert gas, and it is not easy to react with other metal materials and gases. Moreover, due to the cooling effect of the air flow, the heat-affected zone of the weld is small and the deformation of the weldment is small. It is the most ideal shielding gas for argon tungsten arc welding.
(2) Argon is mainly used to effectively protect the molten pool, prevent the air from eroding the molten pool and cause oxidation during the welding process, and at the same time effectively isolate the air in the weld area, so that the weld area is protected and the welding performance is improved.
(3) The adjustment method is determined according to the metal material to be welded, the size of the current, and the welding method: the greater the current, the greater the shielding gas. For active element materials, the protective gas should be strengthened to increase the flow rate.
3. Specification parameters
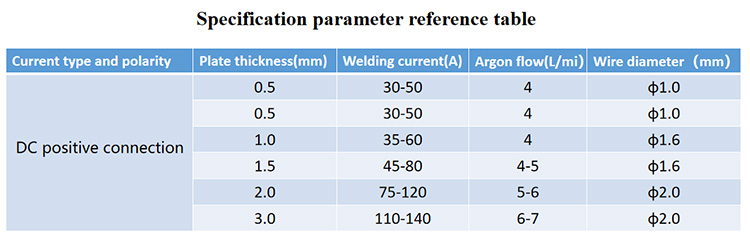
The standard parameters of argon tungsten arc welding mainly include current, voltage, welding speed, and argon gas flow, and their values are related to the type of material to be welded, plate thickness and joint type.
The remaining parameters such as the length of the tungsten electrode protruding from the nozzle are generally 1-2 times the diameter of the tungsten electrode, the distance between the tungsten electrode and the weldment (arc length) is generally 1.5 times the diameter of the tungsten electrode, and the size of the nozzle is determined after the welding current value is determined. Select again.
General stainless steel argon arc welding specifications are as follows:
4. Cleaning before welding
Tungsten argon arc welding is very sensitive to the pollution of the weldment and filler metal surface, so the grease, coating, lubricant and oxide film on the surface of the weldment must be removed before welding.
5. Safety technology
Operators of argon tungsten arc welding must wear head masks, gloves, work clothes, and work shoes to avoid ultraviolet and infrared burns in the arc. Steyr tungsten argon arc welding machines are equipped with high-frequency arc starters. Although the low-power high-frequency high-voltage electricity will not shock the operator, when the insulation performance is poor, the high-frequency electricity will burn the skin of the operator’s hand , and it is difficult to cure, so the insulation performance of the welding handle must be checked frequently. During argon tungsten arc welding, ventilation in the welding area should be enhanced.
Note: The main thing is to be skilled and dexterous. The thickness of the board, the time of clicking, and the current are all related, and they need to cooperate with each other.
When welding, don’t point the needle point at the welding place at the beginning, and hit it empty first to discharge the air in the pipe, so that the welding will not blow up and there will be no black spots. A few seconds, in this way, the stainless steel is protected by argon gas during cooling, so it will not be black, and even the washing water and polishing sheet are saved. This can only be used for spot welding. If you drag welding for a long distance, there is no way. The board will definitely change color. You have to wait for polishing and cleaning.
Post time: May-16-2023